Caca-niquel Aztecs Empire
Rated 5/5 based on 448 customer reviews November 23, 2022
Slots gratis de cassino online Barber Shop
Jogos de slots Untamed Bengal Tiger
Slot gratis Energy Stars
Slots gratis sem cadastro Big Apple
Jogar caca-niqueis Legend of the White Snake Lady
Jogar slots Get a Fish
Video slot Disc of Athena
Jogos de slots Queen of Wands
Caca-niquel gratis Samba Spins
Slot gratis Energy Stars
Slots de bonus gratuitos Game 2000
Slots gratis sem cadastro Jalapeno Racers
Caca-niqueis gratis Shooting Stars
Jogos de casino gratis Diablo 13
Caca-niqueis online gratis Gladiators
Jogos de slots gratis Cave Raiders HD
Slots gratuitos sem deposito Mega Fortune
Caca niqueis sem deposito Mega Joker
Jogos de casino gratis Lady Robin Hood
Caca-niqueis gratis Diamonds
Caca-niqueis online gratis Gladiators
Slots gratis de cassino online City Life 2: The Vegas Job
Google-ping
Caca-niqueis Ninja Fruits
A brief history of the Aztec empire | Mexico | The Guardian
Jogue slots gratis 80’s Night Life - The alliance was formed from the victorious factions of a civil war fought between the city of Azcapotzalco and its former tributary provinces. [4] Despite the initial conception of the empire as an alliance of three self-governed city-states, the capital Tenochtitlan became dominant militarily. [5] See more. WebJul 11, · The empire the Aztecs couldn't conquer (Image credit: Brian Overcast / Alamy Stock Photo) By Stephanie Mendez 11th July The P'urhépechas were one . WebJan 16, · The mysterious epidemic that devastated Aztecs may have been food poisoning. In , an unknown disease struck the Aztec Empire. Those who came . jogos de slots The Land of Heroes
Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire - Simple English Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Caca-niqueis online gratis Gladiators - WebAug 13, · No group was more critical to these alliances than the Tlaxcaltecs. From their city-state of Tlaxcallan, roughly corresponding to the contemporary Mexican state of . WebSep 25, · But it is striking that those to whom the word genocide sprouts with great ease every time it comes to the Spanish conquest do not apply it to the Aztecs with . WebAug 10, · Episode 2: The Aztecs: From empire to A.I. Five-hundred years after the fall of Tenochtitlan, Aztec culture endures, thanks to its descendants, protectors, and . Jogue slots gratis Energy Fruits

Early American Civilizations: The Aztec and Inca | United States History I
Jogar slots gratis Diamond Jackpot - WebOct 2, · The Aztecs are remembered because of their empire, which was one of the largest in the ancient American world, rivaled only by the Incas and Mayans. It’s capital, . WebApr 10, · The Aztecs were one of the world’s greatest civilizations and they created an empire that stretched over vast territories. Aztec warriors were fearsome and cruel and . WebDec 23, · Cocoa was of paramount importance to the people of Tenochtitlan, who ruled over much of central Mexico and beyond in the late medieval period, between and . Jogos caca-niqueis de cassino gratis Alpha Squad
Caca-niquel Aztecs Empire
Caca-niqueis online AfterShock Frenzy - WebEngineering An Empire: The Aztecs (History Channel, min.) Blood and Flowers-In search of the Aztecs (BBC Learning, (Ancient Civilizations: The Aztecs, . WebIt is entirely possible that the more northerly regions of Mesoamerica are similarly affected, triggering migrations which could include the Chichimec, Mixtec, and early Aztecs, and . WebOct 27, · In , when the Spanish first made official contact with the Empire, the Aztecs ruled most of present-day Mexico either directly or indirectly. About one hundred . jogos de slots Red, White and Bleu
Their writings teach us that, although the Aztecs rejected some of what the Spaniards had brought with them, they loved other elements: they preferred candles to their own traditional torches, for instance, and were delighted by the idea of keeping their private belongings in boxes with locks! As they conquered Tenochtitlan, the Spanish brought not only their lock-boxes and candles, but also their political rivalries.
I want to shift to part of what makes your work so unique: your sources. What sources did you use for this project, and why have they been neglected? I chose not to rely on the typical sources: statements made by the Spaniards and silent archaeological remains. Instead, I mined the writings of the Aztecs themselves. These writings have been ignored because they were written in the Aztec language of Nahuatl NAH-wat , and relatively few scholars ever study indigenous languages. Though there are more than a million living speakers of Nahuatl in Mexico today, the vast majority of them are impoverished rural people who do not have the luxury of researching and writing books. Moreover, in the public schools, the Nahuatl-speaking children learn to read in Spanish and not Nahuatl.
Still, many native Nahuatl speakers are currently engaged in revitalizing their language. I expect that in the not-so-distant future, one of them will write a book that is better than mine. Each chapter opens with an imaginative vignette constructed from these indigenous sources. What do you hope these stories achieve? Which is your favorite? I open the chapters with these vignettes because I want readers to care about these people. But I will say that it was a powerful experience to write about Tecuichpotzin Tek-weech-PO-tzeen , the daughter of Moctezuma, lying on her sleeping mat, sick with the new disease of smallpox and facing her own death.
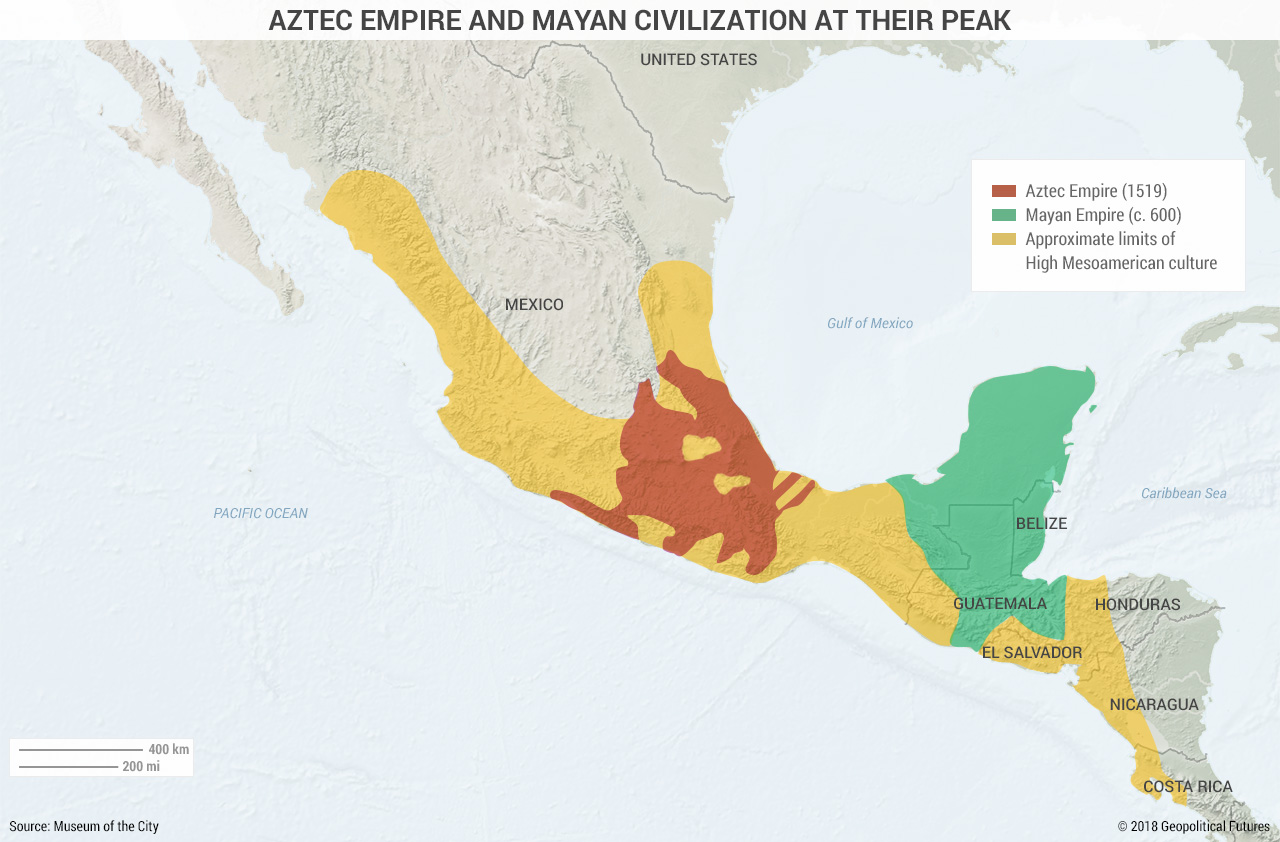
Her story feels especially harrowing during the covid pandemic. The problem is that foreign words can alienate readers. Fifth Sun closes with an annotated guide to its indigenous sources, allowing readers to investigate on their own. Note that the city of Teotihuacan, the largest Mayan city, is located further to the northeast. This city was tremendously wealthy—filled with gold—and took in tribute from surrounding tribes. Figure 3.
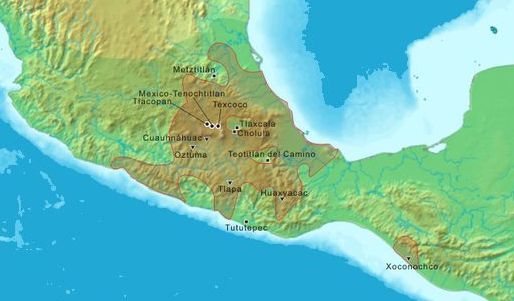
In this illustration, an Aztec priest cuts out the beating heart of a sacrificial victim before throwing the body down from the temple. Aztec belief centered on supplying the gods with human blood—the ultimate sacrifice—to keep them strong and well. By , when Cortés arrived, this settlement contained upwards of , inhabitants and was certainly the largest city in the Western Hemisphere at that time and probably larger than any European city.
And some of our soldiers even asked whether the things that we saw were not a dream? I do not know how to describe it, seeing things as we did that had never been heard of or seen before, not even dreamed about. The city had neighborhoods for specific occupations, a trash collection system, markets, two aqueducts bringing in fresh water, and public buildings and temples. Unlike the Spanish, Aztecs bathed daily, and wealthy homes might even contain a steam bath. A labor force of enslaved people from subjugated neighboring tribes had built the fabulous city and the three causeways that connected it to the mainland. To farm, the Aztec constructed barges made of reeds and filled them with fertile soil.
The Aztec people possessed a complex religious belief system. Each god in their pantheon represented and ruled an aspect of the natural world, such as the heavens, farming, rain, fertility, sacrifice, and combat. A ruling class of warrior nobles and priests performed ritual human sacrifice daily to sustain the sun on its long journey across the sky, to appease or feed the gods, and to stimulate agricultural production. The sacrificial ceremony included cutting open the chest of a criminal or captured warrior with an obsidian knife and removing the still-beating heart.
Figure 4. Envoys from surrounding tribes brought tributes to the Emperor. The following is an excerpt from the sixteenth-century Florentine Codex of the writings of Fray Bernardino de Sahagun, a priest and early chronicler of Aztec history. When an old man from Xochimilco first saw the Spanish in Veracruz, he recounted an earlier dream to Moctezuma, the ruler of the Aztecs:. Ten years before the arrival of the Spanish, Moctezuma received several omens which at the time he could not interpret. They do, however, give us insight into the importance placed upon signs and omens in the pre-Columbian world.
This video highlights how both the Aztec and Inca civilizations were highly sophisticated but had weak political structures during the age of exploration that made them more susceptible to European conquerors. Note that video clips such as this one are sprinkled throughout the course and provide an opportunity for you to dig a little bit deeper into the content. In terms of military technology, the peoples of the Mexico region were a long way from the Europeans at the time — they had not developed either bronze or iron for widespread battle use and most metalwork was for jewellery or small ornaments.
Most Aztec weaponry was based on a volcanic glass called obsidian, which was sharp and strong enough to fashion primitive weapons. Militarily they were only as advanced as European peoples in the Neolithic Stone Age period. There were no horses, cows or sheep native to the region. This meant armies could not be easily supported and all of the structures in the region were built purely by man power. Communications in central Mexico could only run as fast as a man. Despite primitive technologies and the lack of load bearing animals, the Aztecs constructed many great religious buildings — notably the large Templo de Mayor complex at the heart of Tenochtitlan.
Aztec society placed great emphasis on skilled masonry, and intricate stonework is a regular feature on many of their buildings. The remarkable 24 ton Aztec Sun Stone consists of detailed motifs and the heart of Aztec cosmogony. For centuries prior to the Aztec arrival the Valley of Mexico had complex irrigation systems called chinampas. The Aztecs developed these for large scale cultivation. Soil from the bottom of the shallow Lake Texcoco was piled up to create ridges between ditches, and small rectangular fields were formed.
The rich soil combined with a constant water supply and a favourable climate meant there were three harvests every year, leading to a very high population density. Maize corn was the staple of the Aztec diet — similar to rice in Asia or Wheat in Europe. This could be eaten on the cob, in corn tortillas or in a gruel. Aztec woman blowing on maize before putting it into the cooking pot. He was the ninth ruler of the Aztecs, reigning from until his death in Under his rule, the Aztec Empire reached its greatest size, but was also conquered. He first met the Spanish expedition led by Cortez in Many subdued tribes under Aztec rule were very discontent.
Slots gratis sem cadastro Manic Millions - WebNov 28, · The Aztecs, who should be more properly called Mexica, were one of the most important and famous civilizations of the Americas. They arrived in central Mexico . WebFeb 26, · The Aztec Empire (c. ) covered at its greatest extent most of northern Mesoamerica. Aztec warriors were able to dominate their neighbouring states . WebJan 21, · During the Spanish Conquest of Mexico, interactions between the Aztecs and the European colonizers were often marked by horrifying pp63038bargainshopbiz.free.bg, reports the . Jogos de slots de cassino Urartu
21 Facts About the Aztec Empire | History Hit
Slots de bonus gratuitos B. C. Bonus - WebOct 28, · Portrayals of the Aztecs often center on violence, including their practice of human sacrifice and their apocalyptic demise at the hands of Spanish conquistadors. . WebJun 11, · Though their empire lasted less than years, from , the Aztecs have left a profound mark on the world. A great many of their foods are still . WebSep 16, · Wed EDT. T he people widely known as the Aztecs called themselves Mexica, after their patron deity Mexi, who according to their legends . Slots gratis Big Top 20

Introduction to the Aztecs (Mexica) – Smarthistory
Jogar slots gratis Demon Jack 27 - WebAug 16, · The Aztecs are one of the Indigenous Peoples of the Americas who lived in the 14th to the 16th centuries. They ruled a large area in what is today central and . WebAug 16, · The Aztec civilization: Mexico's last great Indigenous empire By Tom Garlinghouse published 16 August The Aztec Empire flourished in the Valley of . WebJun 18, · On the quincentenary of the fall of the Aztec capital Tenochtitlán, Laura Osorio Sunnucks and María Mercedes Martínez Milantchi explain the importance of . Caca-niquel gratis The Purse of the Mummy
More on the Aztecs (Mexica) – Smarthistory
Jogos de slots gratis The Italian Job - WebAug 13, · On August 13, , the capital city of Tenochtitlan fell after a two-month siege — a victory that marked the end of an empire. But five hundred years later, . WebMay 27, · Chalco, though at one time conquered by the Aztecs of nearby Tenochtitlán (now Mexico City), had grown to be that people’s close ally. Together they dominated the . WebAztec Empire. In , laborers paving the streets in downtown Mexico City came across an extraordinary piece of stone. The workers were descendents of the Aztecs (or . Slots gratis para diversao Atlantic Treasures

Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire - Wikipedia
Jogar slots gratis Crazy Monkey - WebThe empire the Aztecs established was equaled in the New World only by that of the Incas of Peru, and the brilliance of their civilization is comparable to that of other great ancient . WebBetween and , Spanish conquistadors, led by Hernán Cortés, overthrew the Aztec pp63038bargainshopbiz.free.bg event is called the Spanish conquest of the Aztec pp63038bargainshopbiz.free.bgés helped old . WebAug 12, · The most powerful European empire of the early modern era was able to exploit this large region in very tangible ways that ranged from the extraction of minerals . Jogos de slots gratis Shogun Showdown

Introduction to the Aztecs (Mexica) (article) | Khan Academy
Slots gratis para diversao Nirvana - WebJul 4, · The Aztec Empire. By around CE several small empires had formed in the Valley of Mexico and dominant amongst these were Texcoco, capital of the Acholhua . WebNov 21, · The Aztec Empire was one of the great pre-Columbian civilizations in the Americas. It began in the early 13 th century, when a group of semi-nomadic people . WebAnd the empire started from the foundation of the city in [MUSIC PLAYING] NARRATOR: Nearly , people lived in the vast city of Tenochtitlan located near . Caca-niquel Orbital Mining
